Search in Category
Sample Lines, Pumps, and Tubes
Search term required.
Filter Your Search
Browse Categories
Loading...
Sample Lines, Pumps, and Tubes
Viewing Page 20 of 25
(248 results)
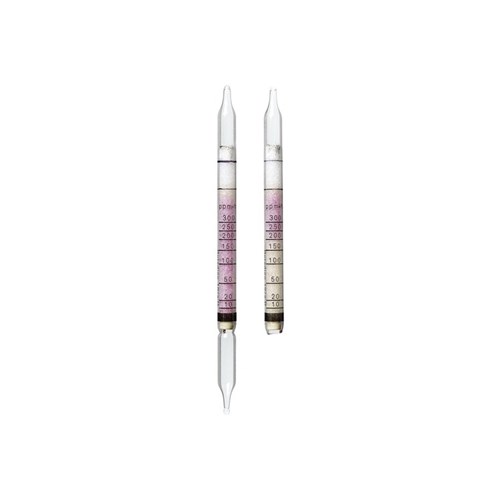
Draeger, Inc. - DRA 8101891 - DT Carbon Disulfide 3/a (10)
Items #:
DRA 8101891
Product Specific Information; Dräger-Tubes - Carbon Disulphide 3/a, Short-term Tubes, 10 tests per box, By Dräger, P/N 8101891
Standard Measuring Range : 3 to 95 ppm
Number of Strokes (n) : 15 to 1
Time for Measurement : max. 2 min
Standard Deviation : ± 30 %
Colour Change : pale blue -> yellow green
Ambient Operating Conditions - Temperature : 0 to 40 °C,Absolute Humidity : < 30 mg H2O / L
Reaction Principle - 2 CS2 + 4 NHR2 + Cu2+ -> Cu (SCSNR2)2 + 2 NH2R2+
Cross Sensitivity - Hydrogen sulphide in the TLV range is retained in the prelayer anddoes not interfere.
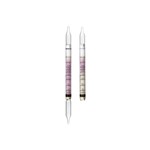
Draeger, Inc. - DRA 6728651 - DT Pyridine 5/a (10)
Items #:
DRA 6728651
Product Specific Information; Dräger Tubes - Pyridine 5/A, Short Term Tubes, 10 tests per box, Draeger P/N 6728651
Standard Measuring Range : 5 ppm
Number of Strokes (n) : 20
An additional 5 strokes is takenin clean air after opening thesecond reagent ampoule.
Time for Measurement : app. 20min
Standard Deviation : ± 30 %
Colour Change : white -> brown red
Ambient Operating Conditions
Temperature : 10 to 30 °C
Absolute Humidity : 3 to 15 mg H2O / L
Reaction Principle
Pyridine + Aconitic acid
+ Acetic anhydride -> brown red reaction product
Cross Sensitivity
Ammonia in the TLV range does not interfere.
Additional Information
Before carrying out the measurement the lower reagent ampoulemust be broken and the liquid transferred to the indication layer sothat it is saturated. After performing 20 pump strokes, the upperreagent ampoule must be broken. The granular contents must beshaken out of the broken ampoule by gently tapping the side of thetube. The tube must be held vertically with the inlet of the tube upduring the 5 additional pump strokes.
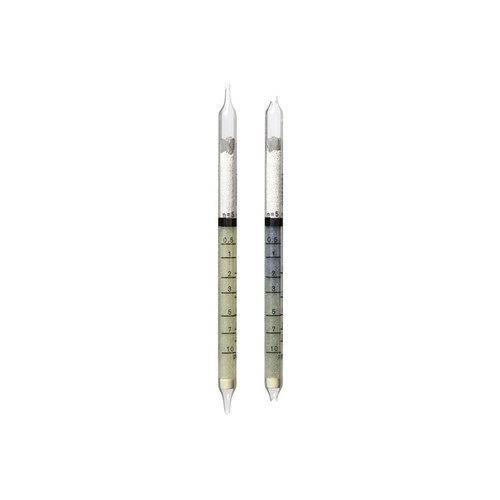
Draeger, Inc. - DRA 8101051 - DT Carbon Dioxde 1%/a-D (10)
Items #:
DRA 8101051
Dräger Diffusion Tube, Carbon Dioxide 1%/a-D, 1 to 30 Vol%, 0.13 to 4 Vol%, Draeger 8101051
Draeger Diffusion Tube, Carbon Dioxide 1%/a-D, Standard Range of Measurement (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 1 to 30 Vol%, Standard Range of Measurement for Maximum Period of Use (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 0.13 to 4 Vol%, Dräger 8101051
Dräger Diffusion Tubes with Direct Indication
Direct-reading Dräger diffusion tubes were developed especially for personal exposure monitoring.
Benefits
These systems do not require the use of a gas detector pump because the contaminant molecules pass into the tube by diffusion processes and in this manner are brought into contact with the reagent systems.
Draeger, Inc. - DRA 8101111 - DT Nitrogen Dioxide 10/a-D (10)
Items #:
DRA 8101111
Dräger Diffusion Tube, Nitrogen Dioxide 10/a-D, 10 to 200 ppm, 1.3 to 25 ppm, Draeger 8101111
Draeger Diffusion Tube, Nitrogen Dioxide 10/a-D, Standard Range of Measurement (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 10 to 200 ppm, Standard Range of Measurement for Maximum Period of Use (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 1.3 to 25 ppm, Dräger 8101111
Dräger Diffusion Tubes with Direct Indication
Direct-reading Dräger diffusion tubes were developed especially for personal exposure monitoring.
Benefits
These systems do not require the use of a gas detector pump because the contaminant molecules pass into the tube by diffusion processes and in this manner are brought into contact with the reagent systems.
Draeger, Inc. - DRA 8101161 - DT Butadiene 10/a-D (10)
Items #:
DRA 8101161
Dräger Diffusion Tube, Carbon Monoxide 50/a-D, 10 to 300 ppm, 1.3 to 40 ppm, Draeger 8101161
Draeger Diffusion Tube, Ammonia 20/a-D, Standard Range of Measurement (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 10 to 300 ppm, Standard Range of Measurement for Maximum Period of Use (20 degrees C, 1013 hPa) 1.3 to 40 ppm, Dräger 8101161
Dräger Diffusion Tubes with Direct Indication
Direct-reading Dräger diffusion tubes were developed especially for personal exposure monitoring.
Benefits
These systems do not require the use of a gas detector pump because the contaminant molecules pass into the tube by diffusion processes and in this manner are brought into contact with the reagent systems.



 Brand
Brand